An asteroid or meteor is more likely to hit Earth because Earth is a lot bigger than the Moon, giving a meteoroid more area to hit! But we can see many thousands of craters on the Moon and we only know of about 180 on Earth! Why is that?
The truth is both the Earth and the Moon have been hit many, many times throughout their long 4.5 billion year history.
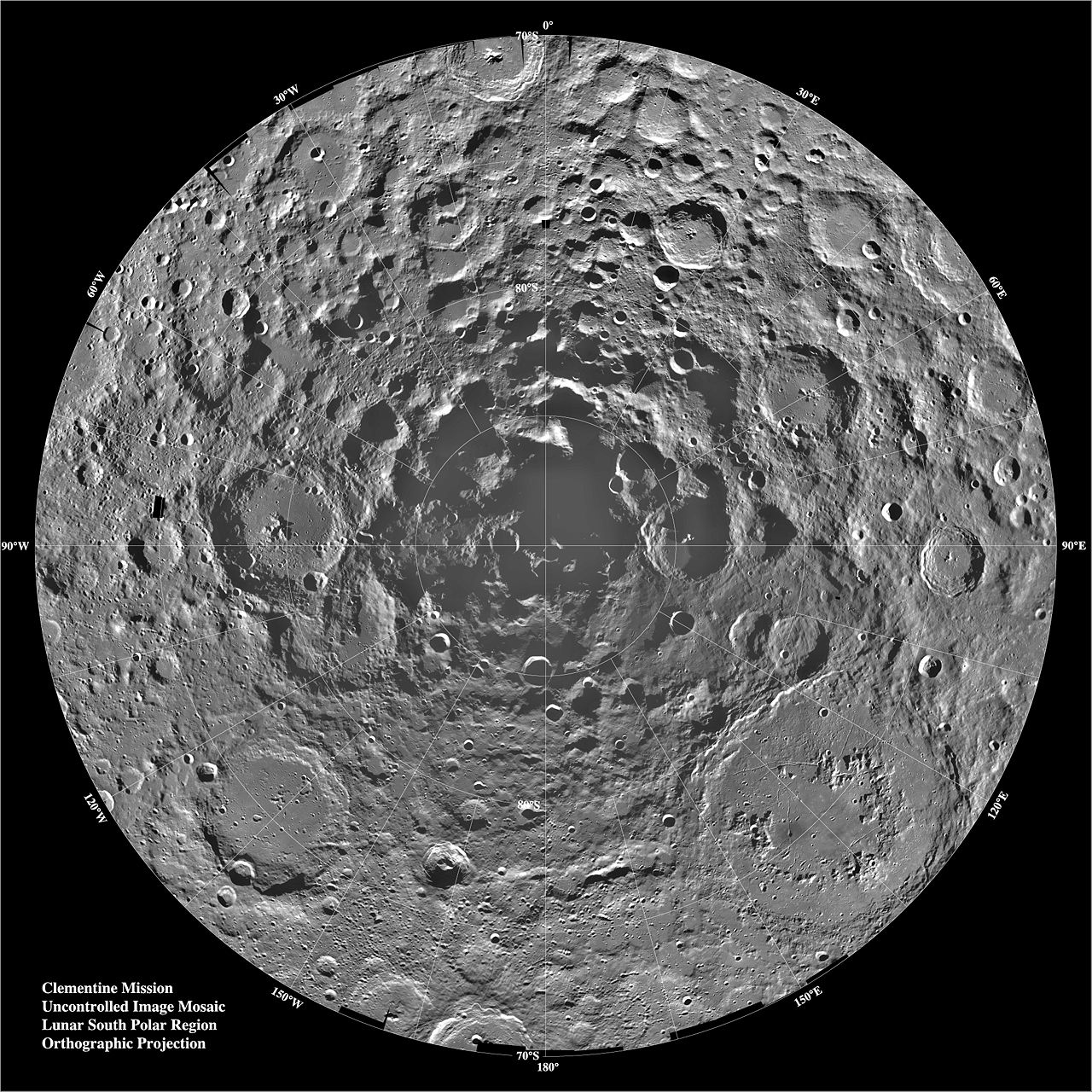
This view of the Moon's cratered South Pole was seen by NASA's Clementine spacecraft in 1996. Credit: NASA/JPL/USGS
Where did all of Earth's craters go?
The main difference between the two is that Earth has processes that can erase almost all evidence of past impacts. The Moon does not. Pretty much any tiny dent made on the Moon’s surface is going to stay there.
Three processes help Earth keep its surface crater free. The first is called erosion. Earth has weather, water, and plants. These act together to break apart and wear down the ground. Eventually erosion can break a crater down to virtually nothing.
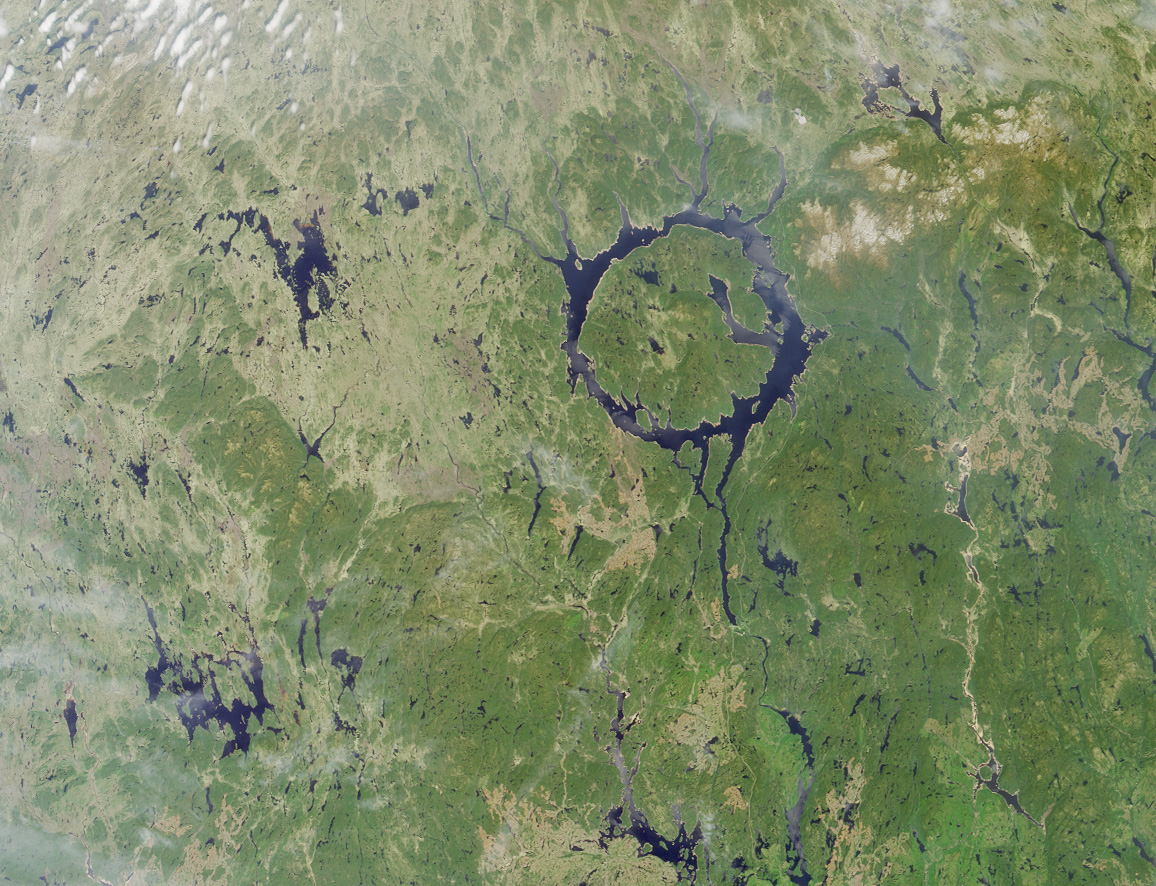

Lake Manicouagan, a ring-shaped lake in Quebec, Canada, is all that remains of a crater from a massive impact over 200 million years ago. Credit: NASA/GSFC/LaRC/JPL/MISR Team
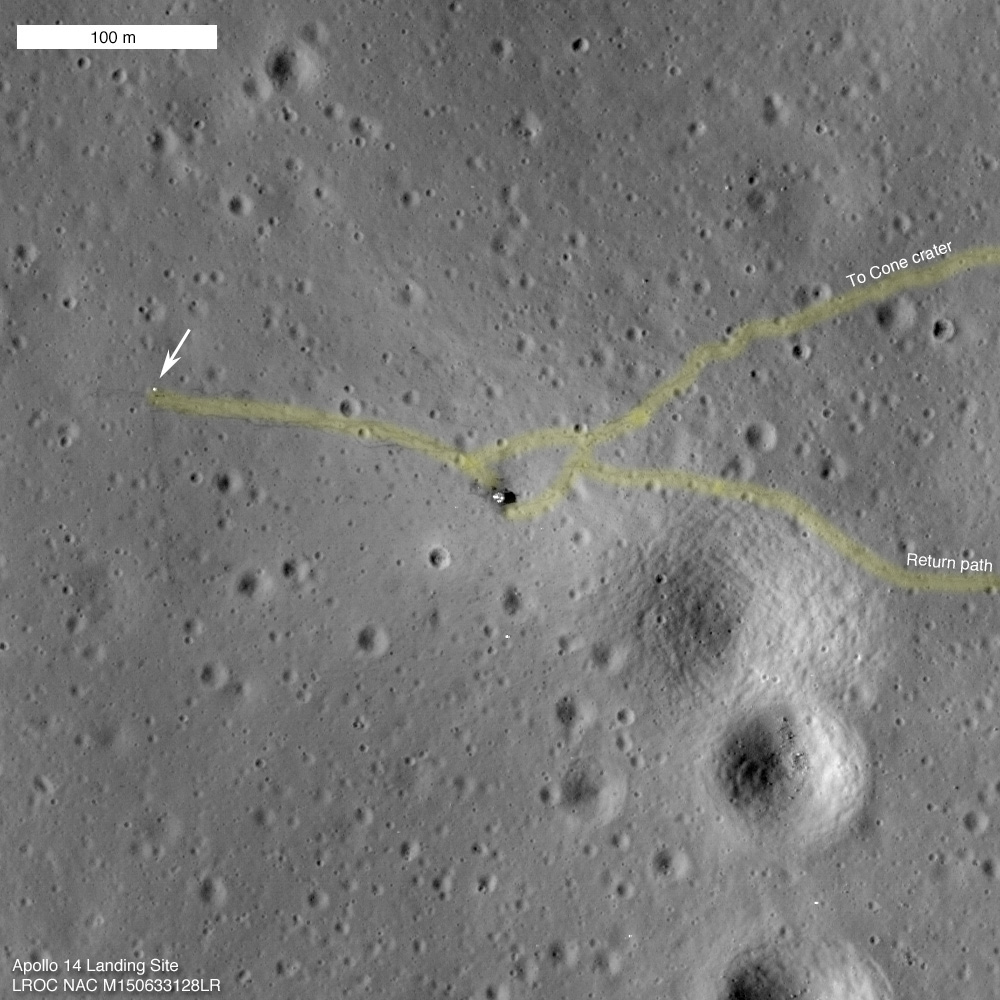

Though they were made in 1971, these Apollo 14 astronauts' tracks were easily viewed from a NASA spacecraft in orbit around the moon in 2011 (tracks highlighted in yellow). Credit: NASA/LRO
The Moon has almost no erosion because it has no atmosphere. That means it has no wind, it has no weather, and it certainly has no plants. Almost nothing can remove marks on its surface once they are made. The dusty footsteps of astronauts who once walked on the Moon are still there today, and they aren’t going anywhere anytime soon.
The second thing is something called tectonics. Tectonics are processes that cause our planet’s surface to form new rocks, get rid of old rocks, and shift around over millions of years.
Because of tectonics, the surface of Earth is recycled many times throughout its long history. As a result, very few rocks on Earth are as old as the rocks on the Moon. The Moon has not had tectonics for billions of years. That’s a lot more time for craters to form and stay put.
The third thing is volcanism. Volcanic flows can cover up impact craters. This is a major way impact craters get covered up elsewhere in our solar system, but it is less important than the recycling of crust here on Earth. The Moon once had large volcanic flows way in the past that did cover up many of the bigger earlier impacts, but it has been without volcanism for around three billion years.
A powerless Moon
The Moon may attract fewer bits of space rock than the Earth, but the Moon is powerless to do anything about it after it has been hit. Once something hits the Moon, that event becomes frozen in time. Earth, on the other hand, simply brushes these impact craters off and moves on with its life.
No wonder there are so many craters on the Moon compared to Earth!
Comments
Post a Comment